Circular Motion Velocity Formula / 5.3: Velocity, Acceleration, and Force - Physics LibreTexts - Objects moving in uniform circular motion have a constant (uniform) speed and a changing velocity.
Circular Motion Velocity Formula / 5.3: Velocity, Acceleration, and Force - Physics LibreTexts - Objects moving in uniform circular motion have a constant (uniform) speed and a changing velocity.. Let's know more about the critical velocity concept here! Is the radius of the circular path, and. Any object travelling on a circle will return to its original starting point in the period of one revolution,. Is the time period for one revolution. Circular motion definition circular motion is the movement of an object in a circular path.
The formulas that correspond to this type of motion. Have you ever observed a rotating fan or a wheel of a moving bicycle? Note that, if you solve the first expression for r, you get. Velocity is a measure of how quickly an object moves. Circular motion formulas, which are used for calculations, are given below.
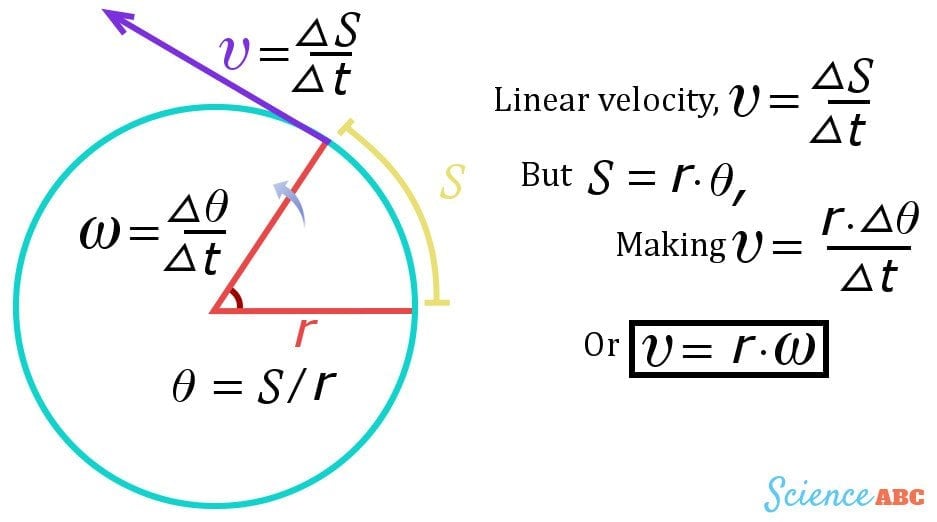
You know that average velocity is displacement divided by interval.
A straight line drawn from the circular path to the center of the circle will always be perpendicular to the tangential velocity. Uniform circular motion assumes that an object is moving (1) in circular motion, and (2) at constant speed. This velocity that will force the mass at the highest point i.e. At all moments in time, that direction is along a line tangent to the circle. In physics, circular motion is rotation along a circle: The radius of its motion is 2.0 m and its period is 5.0 s. In uniform circular motion, what is the angle between the acceleration and the velocity? Velocity definition states that it is the rate of change of the object's position as a function of time. Critical velocity formula is expressed as v1 = √(gr) where g is the acceleration due to gravity and r is the radius of the vertical circular path being. If it acts along the direction of velocity, it will increase its speed, on the other hand if it acts opposite to the direction of velocity it. Section 4.2 velocity of a circular motion. Introduction to velocity and acceleration in cylindrical coordinate system. The concept of the period and frequency in the u.c.m.
A circular path or a circular orbit. They can also be measured in something called radians*, where. Any object travelling on a circle will return to its original starting point in the period of one revolution,. A straight line drawn from the circular path to the center of the circle will always be perpendicular to the tangential velocity. Such change in direction of velocity involves acceleration of the moving object by a centripetal force 1 formulas for uniform circular motion.
Note that, if you solve the first expression for r, you get.
Such change in direction of velocity involves acceleration of the moving object by a centripetal force 1 formulas for uniform circular motion. A circular path or a circular orbit. This velocity that will force the mass at the highest point i.e. C to complete the circular path is known as 'critical velocity'. Critical velocity formula is expressed as v1 = √(gr) where g is the acceleration due to gravity and r is the radius of the vertical circular path being. 1) a sail boat is in a 1000 m race, and it crosses the starting line when it is already at full speed. You know that average velocity is displacement divided by interval. Sample 13.4 using kinematic formulae: Objects moving in uniform circular motion have a constant (uniform) speed and a changing velocity. They can also be measured in something called radians*, where. As acceleration is perpendicular to the velocity, it only changes the direction of velocity, and the magnitude remains. It is one of the fundamental concepts in classical mechanics that considers the motion of bodies. We found in previous section that for small intervals in a circular motion, the displacment is.
Objects moving in uniform circular motion have a constant (uniform) speed and a changing velocity. 1) a sail boat is in a 1000 m race, and it crosses the starting line when it is already at full speed. This is because while its speed is not changing, its velocity is. Critical velocity formula is expressed as v1 = √(gr) where g is the acceleration due to gravity and r is the radius of the vertical circular path being. If you want to put this rule down in the form of a mathematical formula, the velocity equation will be as.
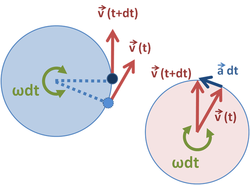
This page is about circular motion velocity,contains is velocity zero during uniform circular motion?,rotational dynamics,critical velocity in vertical circular motion,can somebody explain as how the centripetal acceleration on a object going in a circle with.
The time rate of change of angular displacement (aθ) is called angular velocity. Vc = 2πr / t. This page is about circular motion velocity,contains is velocity zero during uniform circular motion?,rotational dynamics,critical velocity in vertical circular motion,can somebody explain as how the centripetal acceleration on a object going in a circle with. Is the time period for one revolution. Any object travelling on a circle will return to its original starting point in the period of one revolution,. Velocity definition states that it is the rate of change of the object's position as a function of time. Start studying physics circular motion. At all moments in time, that direction is along a line tangent to the circle. You know that average velocity is displacement divided by interval. If an object is moving in a circle at constant speed, it is accelerating. For an object to move along a curved circular path, the direction of its velocity must change. An 800n running back turns a corner in a circular path of r=1m at a velocity of 8 m/s. Is the radius of the circular path, and.
Komentar
Posting Komentar